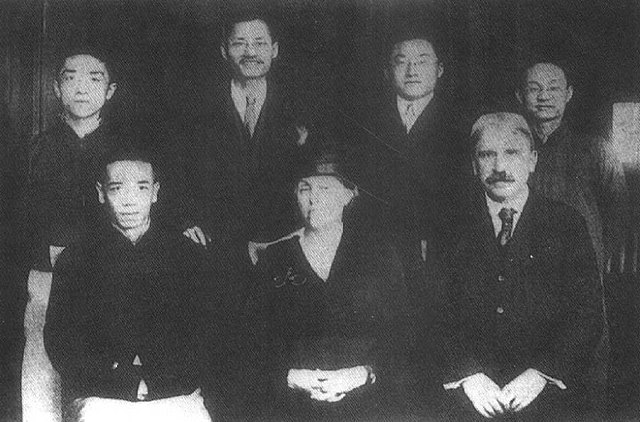
Hu Shih, John Dewey and others in Shanghai, 1919. front row (left to right): Shi Liangcai, John Dewey's wife , John Dewey back row (left to right): Hu Shih, Jiang Menglin, Tao Xingzhi, Zhang Zuoping
Hu Shih, John Dewey and others in Shanghai, 1919. Front Row (left to right): Shi Liangcai, John Dewey’s wife , John Dewey. Back Row (left to right): Hu Shih, Jiang Menglin, Tao Xingzhi, Zhang Zuoping
John Dewey (1859-1952) was an American philosopher, psychologist, and educational reformer who is widely considered one of the most influential figures in modern education. His progressive teaching philosophy, also known as “experiential education,” emphasized the importance of hands-on, student-centered learning that is relevant to the students’ lives.
Dewey’s teaching philosophy was developed during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, a time of significant social and educational change in the United States. Industrialization and urbanization had led to a growing awareness of the need for a more democratic and equitable education system that would prepare students for active participation in a rapidly changing world.
Dewey’s philosophy differed from other philosophers of his time and after, in that it rejected the traditional, teacher-centered approach to education. Instead, he advocated for a more student-centered approach that emphasized the importance of experience, inquiry, and reflection in the learning process. He believed that students learn best when they are actively engaged in the learning process, rather than passively receiving information from the teacher.
One of the key features of Dewey’s teaching philosophy was the idea of “learning by doing.” He believed that students should be given opportunities to engage in real-world, hands-on activities that would allow them to apply what they had learned in the classroom to real-life situations. For example, instead of simply reading about the scientific method, students might design and conduct their own experiments to test a hypothesis.
Another important aspect of Dewey’s philosophy was the idea of “reflective thinking.” He believed that students should be encouraged to reflect on their experiences and think critically about what they had learned. This would help them to develop a deeper understanding of the subject matter and become more independent learners.
Dewey’s teaching philosophy has had a significant impact on education in the United States and around the world. Many schools and universities have adopted his ideas, and his influence can be seen in a wide range of educational settings, from Montessori schools to project-based learning programs.
One example of Dewey’s teaching philosophy in action is the “maker movement,” a growing trend in education that emphasizes hands-on, student-centered learning through the use of technology and engineering. Maker spaces, where students can design, build, and experiment with a variety of materials and tools, are becoming increasingly common in schools and libraries.
In conclusion, John Dewey’s progressive teaching philosophy has had a profound impact on education, emphasizing the importance of hands-on, student-centered learning that is relevant to the students’ lives. His ideas have influenced a wide range of educational settings and continue to inspire educators today.
Reference it APA:
Hussain, M. (2024, July 4). John Dewey’s Progressive Education Philosophy and Its Impact. ZmNoe. https://zmnoe.com/2024/07/04/john-deweys-progressive-education-philosophy-its-impact-and-real-life-applications/
In-text citation: (Hussain,2024)